Buy a URL Today .COM $12.99 | .NET $11.99 | .ORG $19.99 |.CO $34.99

Welcome to How to Buy A URL. This site is dedicated to informing individuals, businesses large or small on how to buy (the correct terminology is “register”) a URL. If you are ready to buy a URL right now, click here Quick Way to Buy a URL, aka Domain Name. If you are interested in learning more about URLs, then please keep reading.
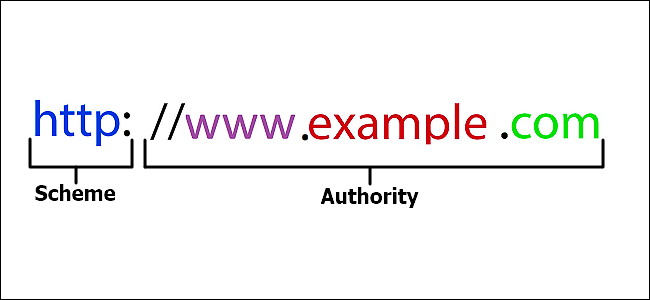
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is essentially a canonical name to identify an address on the World Wide Web, aka the Internet. I know, now you are even more confused when I mentioned the canonical name but don’t worry; it will all make sense. Think of the Internet as just a bunch of phone numbers as destinations when you want to view a certain webpage. There are not really phone numbers on the internet; they are really called IP Addresses (Internet Protocol Address), which look like phone numbers to you and me. These also can be thought of as phone numbers in the sense that you know where you want to go on the internet, and you need to dial it in with your browser (phone). Getting back to the IP Addresses, which are twelve numbers separated into blocks of three separated by a period. For example, an IP address might look like this (123.123.123.123), which resolves to a canonical name, also known as a domain name. So why not just type in the IP Address into your browser every time you want to view a certain website? Well, for one, not everyone can remember their own phone number, let alone a series of twelve numbers that point to a website. It is easier for humans to put meaning to words rather than numbers, and therefore the use of canonical names (aka Domain Names) was born. Let’s face it, would you rather tell someone wanting to see your website that your domain name is 234.239.230.178 or MyDomainName.com?
How do I buy a URL?
Ok, now that you know what a URL is, let’s next talk about how you go about getting one. The first thing you will need to do is find a domain registrar to buy your URL. (Note, in the domain industry, they do not call it buying a URL; they call it registering a domain name. This may help you if you choose to call a sales department for a domain registrar because when you call it “buying a URL,” they may view you as a novice and attempt to sell you stuff that you do not need.) Okay, now you will need to find a Domain Registrar; we use HostOtter.com to register your domain. Please make sure you research the companies you will buy a URL from before taking the big step because some of them have hidden fees. Fortunately, Google made it easy to find domain registrars out there when researching them before buying. All you need to do is search on the keyword “Domain Name,” and you will have an endless list of sites to register your domain at. I would recommend finding a domain registrar called ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) accredited because they have met specific criteria set that ensures they are the reliable registrar. I would also not recommend paying more than $25 per year for a.COM, .NET,ORG,US, .INFO, .WS, .BIZ or.NAME domain names. All domain registrations are registered in one-year increments except for a few foreign TLDs like .CO.UK, which is a two-year minimum. Most domain names can be registered up to 10 years into the future, making it ideal for securing your namespace for the next decade.
What is a Domain Registrar?
A Domain registrar an online business or company that takes orders from customers like you and me on which domain names they want to register. A customer pays the domain registrar a registration fee of anywhere from Free to over $100 per year. The domain registrar then the registrar contacts the Domain Registry for the specific TLD (Top Level Domain) and lets them know that it is now a taken name. (I bet your head is spinning from that last sentence, I know I couldn’t say it three times fast.) The Domain Registry then takes note of the time, domain name, and domain registrar that requested the specific domain name. After you register the domain, it cannot be registered by any other domain registrar. You are probably thinking that this is getting really confusing now. A domain registry is a governing body for their respective TLD (a TLD is just the ending extension of a domain, like .COM, .NET, .ORG, etc.). The Domain Registry is responsible for keeping track of what domain registrars registered, which domains to their customers. This is why you will not be able to register my domain HowToBuyAURL.com with any domain registrar. What happens is the Domain Registrar requests the Domain Registry to find out if the name the customer searched on is available and proceeds accordingly. The Domain Registry charges the domain registrars a specified price, and then the registrars mark it up to turn a profit and cover its costs.